Innovation
3D Printing Technology for Construction
Everything you need to know about 3D printing for construction.
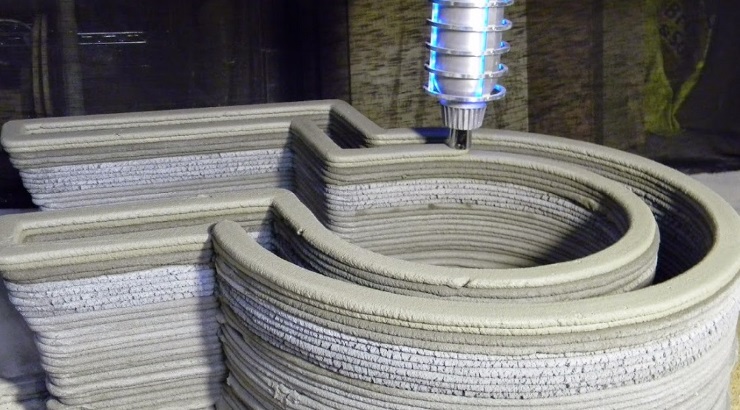
Over the past few years, builders have been warming up to 3D printing construction technology as a solution to the challenges within the industry.
Also known as additive manufacturing, 3D printing for construction involves laying down layers of materials successively to build a complete project.
This technology has been utilized for decades in industries such as aerospace and automotive, but it has only begun to be featured in construction in recent years.
This article explores the benefits and drawbacks of 3D printing in construction. It also considers the various applications of 3D printing for building and discusses the different types of 3D printers.
How it works
3D printing for buildings is done using specialized 3D printers, designed to create large-scale structures layer by layer using additive manufacturing techniques.
A typical 3D printing construction project usually begins with a 3D digital model of the building that needs to be constructed.
The model is virtually sliced into individual layers. Thereafter, the printing robot or gantry system moves along a pre-determined path to place each layer of material, tracing outlines and pushing out material until the entire process is completed.
After finishing one layer, the printer starts work on the next layer on top of the previous one, and this process continues until the whole structure is constructed.
Materials such as concrete, metal, or polymers are commonly used in shaping 3D structures.
The most common technique of 3D printing for building involves a robotic arm that places concrete while moving in a back-and-forth motion. Other techniques include powder binding and additive welding.
Powder binding involves the solidification of powder layers to form the desired object. On the other hand, additive welding involves constructing layers through controlled welding processes, allowing for customized and efficient construction.
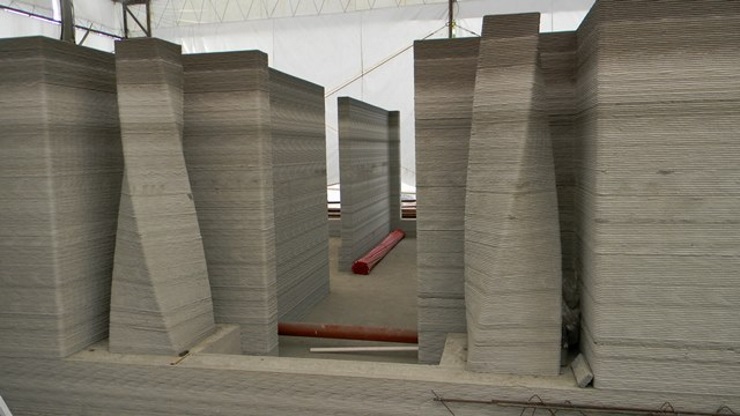

Benefits of 3D printing in construction
Speedy construction: 3D printing technology enables the swift production of parts within hours, accelerating the prototyping phase.
This approach ensures that each stage of the design process occurs more quickly and cost-effectively compared to the traditional machining method.
Thanks to the automation, or partial automation, of this technology, an entire structure can be completed in just a few days.
RELATED: US Firm Delivers World’s Largest 3D-Printed House
Moreover, automated 3D construction printers can work continuously, even at night or bad weather conditions, thereby minimizing downtime.
Reduced human error: 3D printing in construction can greatly reduce errors in construction, leading to safer and superior-quality structures.
Automation of 3D construction printers minimizes the need for human labour, with site workers mainly tasked with overseeing the process.
Versatile designs: This technology allows the creation of complex shapes and designs that are often not possible with traditional manufacturing methods.
Unlike traditional processes that rely on standardized plans and templates, 3D construction printing offers flexibility in producing customized solutions.
Waste reduction: While construction sites are known for generating lots of waste, 3D printing technology uses only the essential materials for each part, resulting in little to no wastage.
Material recycling: One of the key benefits of 3D construction printers is their ability to use recycled materials. This helps to cut building costs while reducing carbon emissions from manufacturing new materials.
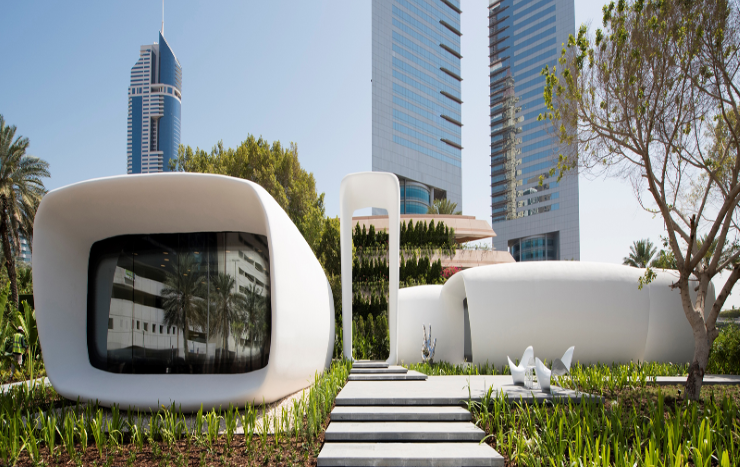

Drawbacks of 3D printing in construction
Costly investment: Acquiring or leasing a 3D printer is quite expensive, especially when factoring in the logistics for transporting the printers to the site.
In addition to the cost of the printer, you also need to take into account the ongoing costs of materials and maintenance. These can make it difficult to justify the technology over traditional construction techniques.
Material constraints: 3D printing in construction is confined to a narrow selection of materials. This limitation affects the range of printable structures and compromises their durability and lifespan.
3D printing in construction is currently limited to a relatively small range of materials, including concrete, plastics, and composites. This restricts the types of structures you can print, as well as their durability and lifespan.
Labour shortage: The expertise and knowledge required for 3D printing of buildings is not yet widely available in the construction marketplace.
This scarcity poses a big problem that hinders the adoption of 3D printing technology in construction projects, thus impeding innovation in the industry.
Quality control: While 3D construction printing can produce complex structures and uncommon designs, maintaining quality can be difficult.
Unlike traditional construction, where supervisors oversee the quality of work, 3D construction printing relies on the precision of the printer.

Types of 3D printers
In construction, 3D printing technology generally falls into two categories: robotic arms and gantry-style setups. Each of these technologies is discussed below:
Robotic arm extruders
Robotic arm extruders, which resemble cranes, are designed to function as a contouring method. These arms move around while depositing materials such as concrete and polymers layer by layer to create a 3D structure.
RELATED: The World’s Finest 3D Printed Homes
Controlled by a computer-aided design (CAD) software, the robotic arm of the 3D printer accurately deposits materials in specified patterns, shapes, and thickness.
Gantry system
This is a large-scale 3D construction printer that uses a gantry system to move the print head along the X, Y, and Z axes. These printers are popular among construction firms printing large structures and buildings.
Gantry 3D printers can print objects more quickly than other types of 3D construction printers, making them well-suited for construction projects.
Despite their capabilities, 3D construction printers are also known for their stability and cost advantages over other types of printers.












